Connect with us
Published
2 years agoon

Mumbai, 12th May 2023: India Exim Bank’s Managing Director, Ms. Harsha Bangari, and Deputy Managing Directors, Mr. N. Ramesh and Mr. Tarun Sharma, announced the Bank’s results for the financial year 2022-23 at a press conference in Mumbai on Friday, May 12, 2023.
Key highlights of the Bank’s performance during 2022-23 are as under:
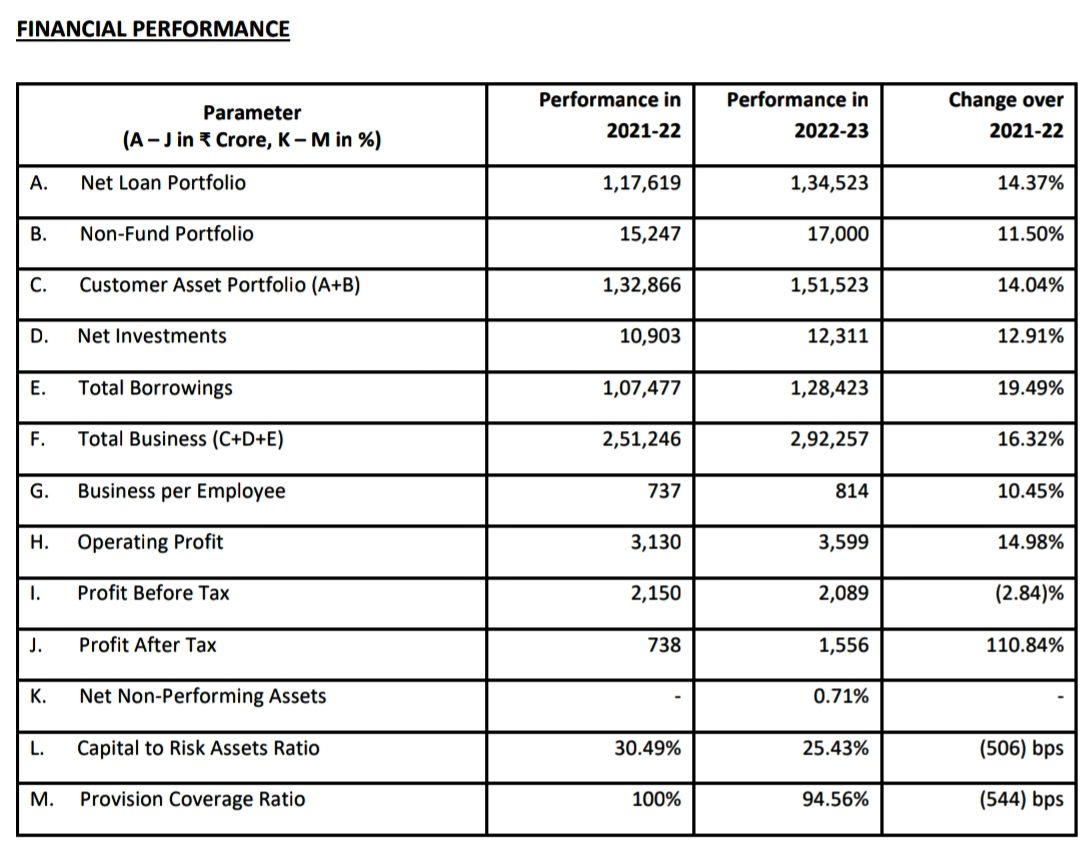
BUSINESS PERFORMANCE
The Bank sanctioned loans aggregating ₹ 79,764 crore during FY 2022-23 to enhance export capabilities of Indian companies and support development priorities of partner countries.
The Bank has a portfolio of 303 Government of India-supported Lines of Credit (LOCs) with credit commitments aggregating US$ 31.85 billion, which are at various stages of implementation.
With ever expanding reach, the LOCs have gained momentum in stimulating economic growth across 68 countries in Africa, Asia, Latin America, Oceania and the CIS region. During FY 2022-23, the Bank supported 37 new contracts valued over US$ 1 billion.
On behalf of the Government of India, the Bank sanctioned seven LOCs, aggregating US$ 670.32 million, to support export of projects, goods, and services from India.
During FY 2022-23, the Bank provided support of ₹ 72,521 crore to Indian companies to build export capacity and boost export competitiveness under the Commercial Business.
Further, the Bank supported 75 project export contracts valued at ₹ 43,421 crore under its commercial portfolio, in 37 countries, propelling project exports to new heights. The Bank has also provided aggregate overseas investment finance of ₹ 67,082 crore to support 671 Joint Ventures / Wholly Owned Subsidiaries, set up by 495 Indian companies in 78 countries, providing opportunities for creating employment, tapping new markets, forging backward and forward integration, accessing raw materials and improving efficiency.
With a focus on supporting MSMEs and facilitating international trade in this segment, the Bank’s Exim Ubharte Sitaare Programme (USP) and a recent initiative, viz. Trade Assistance Programme (TAP), have gained momentum. Under USP, credit facilities aggregating ₹ 638.34 crore were extended to 42 companies in sectors including aerospace, auto, pharmaceuticals, medtech, environmental sustainability, artificial intelligence, Industry 4.0 and consumer durables. In its maiden year, 122 transactions aggregating US$ 304.76 million have been supported under TAP, creating a multiplier effect for incremental exports.
RESOURCES & TREASURY
The Bank raised aggregate resources of ₹ 52,156 crore including foreign currency resources of US$ 3.47 billion during FY 2022 23. The Bank opened the international markets for Indian issuers with a benchmark- sized Sustainability Bond of US$ 1 billion in January 2023, under its ESG Framework. Proceeds of the bond are being used towards projects such as renewable energy, clean transportation, access to essential services and basic infrastructure, affordable housing, water and waste management.
The Bank is rated Baa3 (Stable) by Moody’s, BBB- (Stable) by S&P Global Ratings, BBB- (Negative) by Fitch Ratings and BBB+ (Stable) by Japan Credit Rating Agency. All these ratings are of investment grade or above and are the same as the sovereign rating.
STREAMLINING PROCESSES AND INTRODUCTION OF TECHNOLOGY-ENABLED MONITORING PLATFORM
UNDER LOCs
A refinement of Indian Development and Economic Assistance Scheme (IDEAS) Guidelines has enabled streamlining of processes for monitoring and evaluation of projects financed under the LOCs and Concessional Financing Scheme. A technology-enabled monitoring system for these projects, christened as New E-Tracking & Remote Administration (NETRA), was launched by the Finance Minister, Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman.
FOCUS ON SUSTAINABILITY AND INSTITUTIONAL CAPACITY BUILDING
The Bank has integrated ESG due diligence with overall credit risk assessment framework to identify underlying ESG risks. The Bank was commissioned by Export Barbados for a consultancy assignment for establishing an export credit agency in Barbados. The Department of Commerce, Ministry of Commerce & Industry, Government of India, is also engaging with the Bank to conduct impact assessment of Free Trade Agreements.
EXPORT FACILITATION
The Bank fostered new institutional linkages to facilitate exports from Indian MSMEs. Issuing bank agreements with 12 overseas banks, master risk participation agreements with 10 banks and confirming bank agreements with 4 Indian banks were signed during the year to strengthen the Bank’s Trade Assistance Programme. A master agreement was signed with RXIL Global IFSC Ltd. to finance exports receivables through ITFS platform situated in GIFT City. The Bank under its partnership with leading academic institutions has extended assistance to innovation entrepreneurship arms of IIT Bombay and IIT Delhi to catalyse future growth of companies with export potential identified by these institutions.
The Bank conducted 34 programmes for exporters, with themes such as export awareness, business opportunities, industry, country & region focus, and export potential of Indian states. Workshops were organised for skill development and creating better market access for Bidriware artisans of Karnataka and women artisans from Anoothi India in Rajasthan. Supporting the Government of India’s District as Export Hub initiative, the Bank gave grants for machinery and pesticide kits to chilli farmers of Guntur, Andhra Pradesh.
SOCIAL INITIATIVES
Ten projects / programmes in ten states and two UT were sanctioned in the areas of education & skill development, environment, healthcare & sanitation, and livelihood activities. Some of the notable projects implemented during the year include support to cancer and HIV affected underprivileged children; midday meals for a year to students in Vrindavan;sponsoring students for vocational courses in Mizoram University; installation of solar panels in 20 schools of Solapur; construction of classrooms in Tamil Nadu for children of prisoners, leprosy patients and tsunami victims; and construction of all-weather toilets and training centres in Ladakh for the local weaver community. Two villages in Raigad district of Maharashtra have been identified for an overall improvement of health and education infrastructure, livelihood and skill development under the ‘Dream Village’ initiative. In partnership with SankalpTaru Foundation, the Bank has planted more than 2000 medicinal / fruit-bearing trees across six states.
